Calendar Invite Server (CIS) - Get New Calendar Invite Replies from Email - Technical Overview
1. Executive Summary
This briefing document provides a technical overview of the "Get New Event Reply from Email" function within the Calendar Invite Server (CIS). This function is critical for processing RSVP responses received via email, ensuring that event statuses are updated efficiently and accurately. It leverages several AWS services to achieve a robust and scalable solution for managing event replies.
2. Main Themes and Core Functionality
The primary theme of this function is the automated and efficient processing of event RSVP responses from email. Key functionalities include:
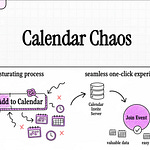
Automated Triggering: The process is initiated by an SQS event, which is itself triggered by an S3 upload notification. This indicates a new email containing an RSVP has been received and stored.
Email Data Extraction: The system retrieves the email content from S3 and extracts crucial event reply details using the iCal format.
RSVP Response Processing: It validates the event method, formats the extracted RSVP data, and publishes a notification to SNS to update the event's status.
Scalability and Reliability: The use of AWS Lambda, S3, SQS, and SNS ensures that the system can handle a high volume of email replies reliably, with built-in mechanisms for error handling and retries.
Clean-up: Successfully processed messages are deleted from SQS to prevent duplicate processing.
3. Key Ideas and Facts
3.1. Purpose of the Function
The "Get New Event Reply from Email" function in the Calendar Invite Server (CIS) "processes RSVP responses received via email. It extracts the event details from the email, formats the response, and sends notifications to update the event’s status."
3.2. AWS Services Utilized
The function relies heavily on several AWS services:
AWS Lambda: "Processes incoming email event replies."
Amazon S3: "Stores email content for extraction."
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service): "Sends notifications for event reply updates."
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service): "Manages email event reply messages in the queue."
3.3. Event Processing Flow
The workflow for processing an event reply from an email follows these steps:
Trigger: "The function is triggered by an SQS event linked to an S3 upload notification."
Extract Email Data: The function "Retrieves the email file from S3" and "Extracts event reply details using the iCal format."
Process RSVP Response: It "Checks if the reply contains a valid event method," "Formats the event reply data," and "Publishes a notification to SNS to update the event status."
Cleanup: "Deletes successfully processed messages from SQS."
3.4. Key Functions and Their Roles
The core logic is encapsulated in several key functions:
lambda_handler(event, *)*: "Processes each record in the SQS event."
process_request_from(record): "Extracts email content and event UID," "Parses the RSVP response using the iCal library," "Sends the formatted response as a notification," and "Removes successfully processed messages from SQS."
get_email_from(record): "Retrieves the S3 file location from the SQS event" and "Extracts email content from the file stored in S3."
extract_event_request_from(email, event_request_uid): "Uses the iCal library to parse event reply details from the email."
send_notification_of_new(event_reply): "Publishes an SNS message containing the formatted event reply."
format_reply_request_from(event_reply): "Extracts and formats key RSVP details" including attendee, dtstamp (timestamp in epoch format), partstat (RSVP status like accepted, declined, tentative), uid (unique event identifier), and prodid (product identifier from iCal).
get_epoch_from(timestamp): "Converts an iCal datetime string into an epoch timestamp."
delete_successfully_processed_sqs(message): "Removes successfully processed messages from SQS to prevent duplicate processing."
3.5. Data Handling
Event Reply Data Format: The data is "Extracted from an email stored in S3" and requires specific fields:
mailto_rsvp: Attendee’s email address.
dtstamp: Timestamp of response.
partstat: RSVP status (accepted, declined, tentative).
uid: Event identifier.
DynamoDB Records: While not updated by this specific function, DynamoDB records are "Used for identifying the corresponding event" via the Event UID.
Environmental Variables:REGION: AWS Region for execution.
NEW_EVENT_REPLY: SNS topic ARN for event reply notifications.
SQS_URL: URL of the SQS queue for processing event replies.
3.6. Error Handling
The function incorporates robust error handling:
Invalid RSVP Data: "If the reply does not contain a valid method, it is ignored."
Processing Failures: "Errors are logged, and failed tasks remain in SQS for retry."
Exception Logging: "Logs errors to facilitate debugging."
4. Conclusion
The "Get New Event Reply from Email" function is a foundational component of the Calendar Invite Server, enabling efficient and reliable processing of RSVP responses. By strategically utilizing AWS services and implementing a clear functional breakdown, it ensures "seamless RSVP tracking for calendar invites."