What is the primary purpose of the "Create New Event Record" function in the Calendar Invite Server (CIS)?
The "Create New Event Record" function is responsible for meticulously processing requests to create new events within the Calendar Invite Server (CIS). Its primary goals are to validate the event organizer's authorization, prepare the event data, securely store it in a database, and trigger appropriate notifications to all relevant parties. Essentially, it's the core mechanism for creating new calendar events within the system, ensuring they are valid and properly propagated.
Which AWS services are fundamentally utilized by the "Create New Event Record" function?
The "Create New Event Record" function relies on several core AWS services to achieve its functionality. These include:
AWS Lambda: This service is used to execute the function itself when an event creation request is triggered, providing a serverless and scalable execution environment.
Amazon DynamoDB: This NoSQL database stores all event records, organizer details, and critical statistics, offering high performance and scalability.
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service): This service is crucial for sending out notifications for newly created events and any subsequent updates, ensuring real-time communication.
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service): This service manages incoming event creation requests, acting as a buffer to ensure reliable processing even under heavy loads.
How does the function ensure that only authorized organizers can create events and manage event limits?
The function incorporates several steps to ensure authorization and effectively manage event limits. When an incoming request is processed, the get_organizer_details function retrieves the organizer's email, subscription status, and existing event statistics. The organizer_can_send function then validates the organizer by checking if their account is suspended, if they have available event slots (to enforce limits), and if they are a paid account (which might bypass specific throttling rules). This multi-layered validation prevents unauthorized event creation, helping to maintain system stability and fairness.
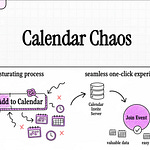
What is the typical flow of an event creation request through the "Create New Event Record" function?
The event processing flow is structured and robust:
Trigger: The function is initiated by an incoming message in an SQS queue.
Organizer Validation: It retrieves and rigorously validates the organizer's details to confirm their authorization.
Event Staging: If authorized, the event data is carefully staged and formatted for storage.
Data Storage: The staged event record is then stored in DynamoDB using transactional writes, ensuring data integrity.
Notifications: Notifications regarding the new or updated event are published to SNS topics.
Message Deletion: Finally, successfully processed messages are removed from SQS to prevent redundant processing.
What types of records are stored in DynamoDB by this function, and what information do they contain?
The "Create New Event Record" function stores three primary types of records in DynamoDB:
Event Record: Identified by pk: event# and sk: event#, this record holds comprehensive event metadata such as timestamps, status, and organizer details.
Organizer Statistics: Identified by pk: organizer# and sk: organizer_statistics#, this record tracks key metrics for each organizer, including the number of events sent and RSVP responses.
Original Event Lookup: Identified by pk: original_event# and sk: original_event#, this record establishes a mapping between the original unique identifier (UID) of an event and the system-generated UID.
How does the function handle errors and ensure reliability in event processing?
The function is designed with built-in error handling and retry mechanisms to ensure reliability. If an error occurs during processing, the failed tasks are not immediately removed from the SQS queue. Instead, they remain in SQS, allowing for automatic retries. Additionally, all errors are meticulously logged, which is crucial for tracking failures, debugging issues, and maintaining a robust event management system.
What are transactional writes in DynamoDB, and why are they used by this function?
Transactional writes in DynamoDB allow for multiple put, update, or delete operations to be performed atomically across one or more tables within the same AWS account and region. This means that either all operations within the transaction succeed, or none of them do. The "Create New Event Record" function uses DynamoDB Transactions to:
Create a lookup entry for the event’s original UID.
Store the main event record.
Initialize event statistics.
Update the organizer’s event count. This ensures data consistency and integrity across related records, preventing partial updates that could lead to an inconsistent state.
What environmental variables are critical for the operation of the "Create New Event Record" function?
Several environmental variables are essential for configuring and operating the "Create New Event Record" function:
REGION: Specifies the AWS Region where the function will execute.
DYNAMODB_TABLE: Defines the name of the DynamoDB table used to store event data.
NEW_EVENT_CREATED: The SNS topic ARN for notifications when a new event is created.
EVENT_UPDATED: The SNS topic ARN for notifications when an event is updated.
EVENT_LIMIT_REACHED: The SNS topic ARN for warnings when an organizer reaches their event creation limit.
EVENT_INVITE_LIMIT: Sets the maximum number of invitees allowed per event.
SQS_URL: The URL of the SQS queue from which event creation requests are received.