Briefing Document: Calendar Invite Server (CIS) - Get New Event Calendar Invite Request from Calendar Client - Technical Overview
1. Overview and Purpose
This document provides a technical overview of the "Get New Event Request from Calendar Invite Email" function within the Calendar Invite Server (CIS). The primary purpose of this function is to automate the processing of event creation, updates, and cancellations initiated via email. It leverages several Amazon Web Services (AWS) to efficiently extract event details from incoming calendar invite emails, determine the request type, and trigger subsequent processing workflows. The goal is to provide a robust and scalable solution for managing calendar event requests received through email.
2. Main Themes and Core Functionality
The central theme revolves around the automated, email-driven processing of calendar event requests using a serverless AWS architecture.
2.1. Event Request Lifecycle (Email-Driven)
The function manages the entire lifecycle of an event request originating from an email, from initial receipt to routing for specific actions.
Trigger: The process is initiated by an "SQS event linked to an S3 upload notification." This implies that emails are first stored in Amazon S3, and this storage event then triggers a message in an SQS queue, which in turn triggers the Lambda function.
Calendar Invite Email Data Extraction: The system "Retrieves the email file from S3" and "Extracts event request details using the iCal format." This highlights the importance of standardized email calendar formats for successful processing.
Request Type Determination: A critical step is to "Determine the request method (request, update, cancel)" to route the event for further action correctly.
Routing to Appropriate Processing: Based on the request method, the function "Routes the request to the appropriate SNS topic for further processing." This decouples the initial email processing from the specific actions (creation, update, cancellation).
Cleanup: "Deletes successfully processed messages from SQS" to ensure messages are not reprocessed and the queue remains clean.
2.2. AWS Services Utilized for Serverless Architecture
The solution heavily relies on serverless AWS components for scalability, efficiency, and reduced operational overhead.
AWS Lambda: This is the core compute service that "Handles the processing of email-based event requests." It executes the code for the function.
Amazon S3: Used for "Stores email content for processing." This acts as the initial landing zone for incoming emails.
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service): Crucial for "Sends notifications for event processing (creation, update, cancellation)." SNS acts as a pub/sub messaging service, routing requests to relevant downstream services.
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service): "Manages event request messages in the queue." SQS provides a reliable buffer for event requests, ensuring messages are processed even if the Lambda function experiences temporary issues.
2.3. Supported Event Request Methods
The function explicitly supports three types of event requests, all originating from the iCal format within the email:
request: "Creates a new event."
update: "Updates an existing event."
cancel: "Cancels an event."
2.4. Key Functions and Their Responsibilities
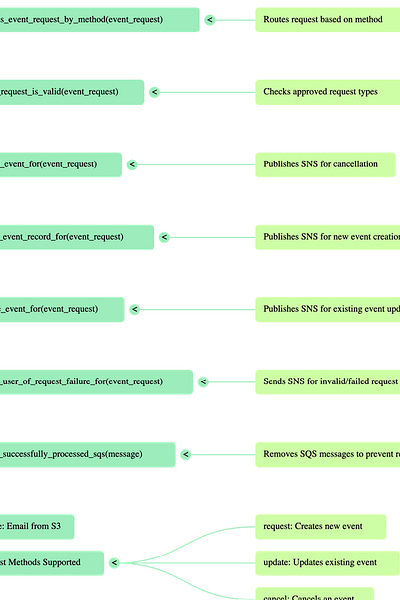
The document details specific functions within the Lambda, illustrating a modular design:
lambda_handler(event, *): The entry point, iterating through SQS records and calling process_request_from.
process_request_from(record): Extracts email content, event UID, determines request type, routes it, and deletes SQS messages.
extract_event_request_from(email, event_request_uid): Parses iCal data and standardizes event fields.
process_event_request_by_method(event_request): Routes the request to specific SNS topics based on its method.
event_request_is_valid(event_request): Validates the request method against approved types.
cancel_event_for(event_request), create_event_record_for(event_request), update_event_for(event_request): These functions publish SNS messages for their respective event actions.
notify_user_of_request_failure_for(event_request): Handles notifications for invalid or failed requests.
delete_successfully_processed_sqs(message): Ensures messages are removed from the queue post-processing.
3. Important Ideas/Facts
iCal Format: The system relies heavily on the "iCal format" for extracting event request details, indicating a dependency on a standardized calendar data exchange format.
Asynchronous Processing: The use of SQS and SNS ensures an asynchronous processing model, enhancing system resilience and scalability. Emails are queued and processed independently, preventing bottlenecks.
Decoupling: The architecture effectively decouples the email ingestion and parsing from the actual event management (creation, update, cancellation) via SNS topics. This allows different services to subscribe to and handle these events independently.
Environmental Variables: Critical configuration parameters like AWS Region, SNS Topic ARNs for various event types, and SQS URL are managed through environmental variables, promoting flexibility and easier deployment.
Error Handling: Robust error handling is integrated:
"Invalid Event Requests: If the request does not contain a valid method, an SNS notification is sent to the requester."
"Processing Failures: Errors are logged, and failed tasks remain in SQS for retry."
"Exception Logging: Logs errors to facilitate debugging."
DynamoDB Reference (for UID Lookup): While this specific function doesn't update DynamoDB, it "Used for identifying the corresponding event," implying that a DynamoDB table stores event records and is consulted using the Event UID.
GitHub as a Wiki: The source itself is from a GitHub Wiki, suggesting that this is internal documentation for a development project (calendarinvite/calendarinviteserver).
4. Summary and Key Takeaways
The "Get New Event Request from Calendar Invite Email" function is a foundational component of the Calendar Invite Server (CIS), providing an automated and resilient mechanism for integrating email-based Calendar Invite event management. It demonstrates a well-architected serverless solution leveraging core AWS services (Lambda, S3, SQS, SNS) to handle the entire pipeline of email event request processing, from ingestion and parsing (using iCal) to intelligent routing and robust error handling. The focus on asynchronous processing, decoupling of concerns, and clear function responsibilities ensures a scalable, maintainable, and efficient system for managing event lifecycle changes initiated via email.