Briefing Document: Calendar Invite Server (CIS) - Bulk Event Invite Functionality
Source: Excerpts from "Chapter 10 ‐ Send Bulk Event Invites ‐ Technical Overview · calendarinvite/calendarinviteserver Wiki · GitHub"
I. Overview of the Send Bulk Event Invites Function
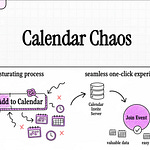
The "Send Bulk Event Invites" function is a core component of the Calendar Invite Server (CIS), designed to process and dispatch a large number of event invitations efficiently. Its primary goal is to ensure that attendees receive "properly formatted calendar invites while tracking invite history and updating event statistics." This function leverages a serverless architecture on Amazon Web Services (AWS) to achieve scalability and reliability.
II. Key AWS Services Utilized
The bulk event invitation process relies heavily on a suite of AWS services working in conjunction:
AWS Lambda: This serverless compute service is the backbone of the function, handling the "bulk invite processing." It executes the code that manages the invitation workflow.
Amazon SES (Simple Email Service): This service is responsible for the actual delivery of the calendar invites. The function "Sends calendar invites to attendees" is directly through SES RAW.
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service): SQS acts as a message queuing service, managing the flow of bulk invite requests. It "Manages bulk invite requests," ensuring that invitations are processed in an orderly and asynchronous manner.
Amazon DynamoDB: This NoSQL database service is used for storing data persistently. It "Stores attendee records and event statistics," providing a reliable way to track invitee information and overall event metrics.
III. Functionality Breakdown and Event Processing Flow
The process of sending bulk event invites follows a defined workflow:
Trigger: The entire process is initiated by an "SQS event notification," indicating that there are new bulk invite requests to be processed.
Extract Invite Details: Upon triggering, the function "Retrieves invite data from the SQS message." A crucial step here is to "check if the attendee has already been sent an invite" to prevent duplicates.
Send Invite: If an invite has not been previously sent, the system "Generates a properly formatted iCal invitation" and then "Sends the invite via SES RAW." The iCal format ensures compatibility with various calendar applications.
Update Event Records: After successfully sending an invite, the function "Stores invitee details in DynamoDB" and simultaneously "Updates invite statistics for the event." This maintains a comprehensive record of attendees and their engagement with the event.
Cleanup: To prevent reprocessing and ensure efficient queue management, the function "Deletes successfully processed messages from SQS."
IV. Key Functions (Code-Level Overview)
The technical overview highlights several critical functions that orchestrate the bulk invitation process:
lambda_handler(event, *): This is the entry point for the Lambda function. It "Iterates through each record in the SQS event" and delegates individual invitation processing to process_request_from.
process_request_from(record): This function is responsible for the core logic of processing a single invite. It "Extracts invitee details," "Checks if the invitee has already been sent an invite," "Sends an invite if necessary," and finally "Deletes the processed message from SQS."
attendee_has_not_been_sent(event_invite): This function specifically "Checks DynamoDB to verify if the attendee has already been invited," preventing duplicate communications.
send_invite_to_attendee(invite): This function handles the actual email dispatch, formatting, and sending "an iCal invite via SES."
get_ical_for(invite): Dedicated to creating the calendar attachment, this function "Generates an iCal formatted invite."
create_record_of_attendee(invite): This function is responsible for data persistence, specifically "Stores the invitee’s information in DynamoDB" and also "Updates event statistics and invite limits."
delete_successfully_processed_sqs(message): This crucial cleanup function "Removes successfully processed messages from SQS to prevent retries."
V. Data Handling and Environmental Variables
DynamoDB Records: Attendee Record: Stored with a primary key pk: event# and sort key sk: attendee#. This record "Stores attendee information, RSVP status, and history."
Event Statistics: Tracks aggregate data such as "the number of invites sent, RSVP responses, and other key metrics."
Environmental Variables: The function relies on several environment variables for configuration:
REGION: Specifies the AWS region where the execution will occur.
DYNAMODB_TABLE: The name of the DynamoDB table used for data storage.
SENDER: The email address used as the sender for invitations.
RSVP_EMAIL: The email address designated for collecting RSVP responses.
SQS_URL: The URL of the SQS queue used to process event invites.
VI. Error Handling
The system incorporates robust error-handling mechanisms to ensure smooth operation and prevent issues:
Duplicate Invites: "If an invitee has already been sent an invite, no duplicate is sent," preventing spam and ensuring a positive user experience.
Email Sending Failures: These are "Logged for troubleshooting but do not halt execution," allowing the system to continue processing other invites even if a few fail.
Exception Logging: General errors are "logged to facilitate debugging," aiding in identifying and resolving issues quickly.
VII. Summary
The "Send Bulk Event Invites" function is a testament to an "efficient handling of large-scale event invitations." Its strategic "integration with AWS Lambda, SES, SQS, and DynamoDB" creates a robust and scalable solution for dispatching calendar invites, meticulously tracking invitation history, and maintaining up-to-date event statistics. This technical overview highlights a well-designed system capable of managing high-volume event communication.