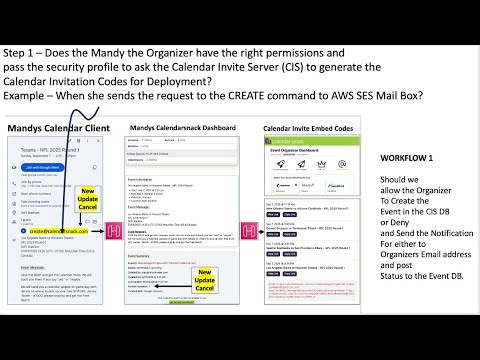
Study Guide: Calendar Invite Server (CIS) - Verify New Event Invite Request
Overview
This study guide focuses on the "Verify New Event Invite Request" function within the Calendar Invite Server (CIS). This core component ensures that all event invitations are appropriately authorized and adhere to defined rules before being sent to attendees. It plays a critical role in maintaining system integrity and preventing abuse.
Key Concepts and Functionality
The Verify New Event Invite Request function serves to validate event invitations. This involves several checks:
Authorization: Confirming the organizer is permitted to send invites.
Invite Limits: Enforcing any restrictions on the number of invites an organizer can send.
Restrictions: Checking for scenarios where an invitation should not be sent (e.g., the invitee has blocked the organizer, the organizer's account is suspended).
AWS Services Utilized
The function leverages several Amazon Web Services (AWS) to achieve its goals:
AWS Lambda: The serverless compute service that executes the invite verification processing.
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service): Used to manage and queue event invite verification requests, ensuring reliable processing.
Amazon DynamoDB: A NoSQL database service employed to store and retrieve event and organizer data, crucial for validation checks.
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service): Publishes notifications for successfully verified invites, initiating the next steps in the invitation process.
Event Processing Flow
The verification process follows a specific flow:
Trigger: The function is activated by an event notification from Amazon SQS, indicating a new invite request is ready for verification.
Retrieve Event Details: Upon being triggered, the function queries DynamoDB to gather all necessary event and organizer information.
Validation Checks: A series of crucial checks are performed:
Verifying that the invitee has not blocked the organizer.
Confirming the organizer's account is active and not suspended.
Ensuring bulk invite requests comply with authorization and invite limits.
Approve or Deny Invite:If all validation checks pass, the invite request is approved, and a notification is published to Amazon SNS.
If any validation check fails, the invite request is denied.
Cleanup: Successfully processed messages are deleted from the SQS queue to prevent redundant retries.
Key Functions and Their Roles
The core logic of the system is encapsulated in several specialized functions:
lambda_handler(event, **): The entry point for the Lambda function. It iterates through SQS records and calls process_request_from.
process_request_from(record): Extracts invite details, queries DynamoDB, runs validation checks, and deletes the processed SQS message.
verified_to_send(request, event): Orchestrates the main validation checks, including blocking status, account suspension, and bulk invite limits.
attendee_has_blocked(organizer, attendee): Queries DynamoDB to determine if an attendee has blocked the specified organizer.
account_is_suspended_for(organizer): Checks DynamoDB for the suspension status of an organizer's account.
bulk_validation_failed(origin, organizer, event): Verifies compliance with permissions and invite limits for bulk invite requests.
send_notification_of_verified(request, event): Publishes an SNS message for approved event invites.
delete_successfully_processed_sqs(message): Removes messages from SQS after successful processing.
Data Handling
DynamoDB Records: The system primarily uses Event Records with the primary key (pk) of event# to store event metadata, including invite limits and organizer details.
Environmental Variables: Critical configuration parameters are managed via environmental variables, such as REGION, DYNAMODB_TABLE, SQS_URL, and NEW_EVENT_INVITE_SNS_TOPIC_ARN.
Error Handling
Robust error handling is implemented to manage various scenarios:
Invalid Invite Requests: Requests missing required fields are logged and skipped.
Authorization Failures: Denied and logged if an organizer or invitee is restricted.
Exception Logging: Errors are systematically logged to aid in debugging and troubleshooting.
Quiz
Instructions: Answer each question in 2-3 sentences.
What is the primary purpose of the "Verify New Event Invite Request" function in the Calendar Invite Server (CIS)?
Which AWS service is responsible for executing the invite verification processing logic?
How does the system ensure that event and organizer data is available for validation checks?
What is the role of Amazon SQS in the event processing flow for new invite requests?
List two specific validation checks performed by the verified_to_send function.
What action does the function take if all validation checks pass for an invite request?
What happens to a message in the SQS queue once it has been successfully processed?
Explain the purpose of the attendee_has_blocked function.
Why are environmental variables like DYNAMODB_TABLE and SQS_URL used in this system?
Describe how the system handles an "Authorization Failure" during the invite verification process.
Answer Key for Quiz
The primary purpose of the "Verify New Event Invite Request" function is to ensure that event invitations are authorized and adhere to defined rules before being sent to attendees. This prevents unauthorized or excessive event invites and maintains system integrity.
AWS Lambda is the AWS service responsible for executing the logic that processes invite verification. It acts as the serverless compute environment where the code for this function runs.
The system ensures event and organizer data is available for validation checks by querying Amazon DynamoDB. DynamoDB stores this crucial information, allowing the function to retrieve details like invite limits and organizer status.
Amazon SQS manages event invite verification requests by acting as a queue. An SQS event notification triggers the "Verify New Event Invite Request" function, and successfully processed messages are deleted from the queue.
Two specific validation checks performed by the verified_to_send function are: checking if the invitee has blocked the organizer, and verifying that the organizer's account is active (not suspended). It also ensures bulk sending requests meet authorization and invite limits.
If all validation checks pass for an invite request, the request is approved. An SNS message is then published, signaling that the event invite can be processed and sent.
Once a message in the SQS queue has been successfully processed, it is deleted from the queue. This action prevents the message from being processed again, ensuring efficient and reliable operation.
The attendee_has_blocked function's purpose is to query DynamoDB to determine if a specific attendee has previously blocked the organizer attempting to send the event invite. This is a critical validation check to respect user preferences.
Environmental variables like DYNAMODB_TABLE and SQS_URL are used to configure the system with dynamic parameters that can change between environments (e.g., development, production) without modifying the code. This promotes flexibility and easier deployment.
If an "Authorization Failure" occurs (e.g., an organizer or invitee is restricted), the invite request is denied. The system then logs this failure, which is important for debugging and understanding why an invitation was not sent.
Essay Format Questions (No Answers Provided)
Analyze the importance of the "Verify New Event Invite Request" function within the broader context of a calendar invitation system. Discuss how its various validation checks contribute to system reliability, security, and user experience.
Describe the interconnectedness of the AWS services (Lambda, SQS, DynamoDB, SNS) used by this function. Explain how each service contributes to the overall event processing flow and how their combined use creates a robust, scalable architecture.
Evaluate the error handling mechanisms implemented in the "Verify New Event Invite Request" function. Discuss the significance of logging invalid requests, authorization failures, and general exceptions for system maintenance and debugging.
Imagine a new requirement arises: event invites should only be sent to attendees residing in a specific geographical region. Outline how you would integrate this new validation check into the existing process_request_from and verified_to_send functions, considering necessary data storage and retrieval.
Discuss the role of the bulk_validation_failed function. Why is it important to have specific checks for bulk invite requests, and what potential issues could arise if these checks were omitted or insufficient?
Glossary of Key Terms
AWS Lambda: A serverless, event-driven compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers.
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service): A fully managed message queuing service that enables you to decouple and scale microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications.
Amazon DynamoDB: A fast and flexible NoSQL database service for all applications that need consistent, single-digit millisecond latency at any scale.
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service): A fully managed messaging service for both application-to-application (A2A) and application-to-person (A2P) communication.
Calendar Invite Server (CIS): The overarching system responsible for managing event invitations.
lambda_handler: The entry point function for an AWS Lambda function, called when the Lambda is invoked.
process_request_from: A key function responsible for extracting invite details, querying data, running validations, and cleaning up messages.
verified_to_send: A core validation function that consolidates checks such as attendee blocks, organizer account status, and bulk invite limits.
attendee_has_blocked: A specific function to determine if an invitee has opted out of receiving invites from a particular organizer.
account_is_suspended_for: A function that checks the status of an organizer's account to ensure it is active.
bulk_validation_failed: A function dedicated to verifying that bulk invitation requests comply with predefined permissions and limits.
send_notification_of_verified: The function responsible for publishing a success message to an SNS topic for approved invites.
delete_successfully_processed_sqs: A cleanup function that removes messages from the SQS queue after successful handling.
Environmental Variables: Configuration settings that are external to the code and can be set at runtime, used for parameters like AWS region, database table names, and queue/topic URLs.
Event Record (DynamoDB): A data entry in DynamoDB that stores metadata related to an event, identified by a primary key (pk: event#).
ARN (Amazon Resource Name): A unique identifier for an AWS resource.
AI Vid
FAQ -
1. What is the primary purpose of the "Verify New Event Invite Request" function in the Calendar Invite Server (CIS)?
The "Verify New Event Invite Request" function is designed to ensure that all event invitations are appropriately authorized and adhere to established rules before being sent to attendees. Its main goal is to prevent the sending of unauthorized, excessive, or otherwise restricted event invites, thereby maintaining the integrity and reliability of the calendar invitation system.
2. Which AWS services are utilized by this verification function?
The function leverages several AWS services to perform its tasks:
AWS Lambda: This serverless computing service handles the core processing of the invite verification requests.
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service): SQS is used to manage and queue incoming event invite verification requests, ensuring reliable delivery and processing.
Amazon DynamoDB: This NoSQL database stores crucial event and organizer data, which is queried during the validation process to fetch necessary information.
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service): SNS is responsible for publishing notifications for invites that have been successfully verified and approved.
3. What are the key validation checks performed during the event invite verification process?
The verification function conducts several critical validation checks to determine if an invite should be sent:
Invitee Block Status: It checks if the invitee has previously blocked the organizer.
Organizer Account Status: It verifies that the organizer's account is active and not suspended.
Bulk Invite Authorization and Limits: For bulk invite requests, it ensures that the organizer has the necessary authorization and that the request complies with any predefined invite limits.
4. How does the system handle an invite request that fails validation?
If any of the validation checks fail (e.g., invitee has blocked the organizer, organizer's account is suspended, or bulk invite limits are exceeded), the event invite request is denied. These failures, along with any other errors like missing required fields or authorization issues, are logged to facilitate debugging and provide a record of why the invite was not sent.
5. What happens to a message in SQS after it has been processed?
After a message representing an event invite request has been successfully processed and either approved or denied, it is deleted from the SQS queue. This cleanup step is crucial to prevent the same message from being processed multiple times, ensuring efficiency and avoiding redundant actions.
6. What kind of data is stored in DynamoDB for this function?
DynamoDB primarily stores event and organizer data essential for the verification process. Specifically, it holds "Event Records" identified by a pk (primary key) in the format event#. These records contain event metadata, including important details like invite limits and organizer information, which are retrieved during the validation checks.
7. How are environmental variables used in the "Verify New Event Invite Request" function?
Environmental variables are used to configure the function's operation and integrate it with AWS services. These include:
REGION: Specifies the AWS region where the function is executed.
DYNAMODB_TABLE: Defines the name of the DynamoDB table used to store event and organizer data.
SQS_URL: Provides the URL of the SQS queue responsible for processing event invite verification requests.
NEW_EVENT_INVITE: Specifies the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the SNS topic to which approved invite notifications are published.
8. What is the overall benefit of this verification function to the Calendar Invite Server (CIS)?
The "Verify New Event Invite Request" function is fundamental to the reliability and security of the Calendar Invite Server. By systematically validating event invitations before they are sent, it actively prevents issues such as spam, unauthorized event creation, and abuse of the system. This pre-sending verification process ensures that only legitimate and authorized invites reach attendees, thereby maintaining event integrity and fostering trust in the calendar invitation platform.