Calendar Invite Server (CIS) Onboarding Briefing
Source: Excerpts from "Chapter 1 ‐ Calendar Invite Server ‐ Onboarding Instructions Technical Overview · calendarinvite/calendarinviteserver Wiki · GitHub"
This briefing outlines the technical overview and onboarding instructions for the Calendar Invite Server (CIS), focusing on its architecture, AWS service utilization, CI/CD pipeline, and key operational aspects.
Main Themes
The core themes of the CIS onboarding instructions revolve around structured setup, AWS cloud integration, automated CI/CD, and robust event processing. The document emphasizes a straightforward, step-by-step approach for developers to deploy and manage the CIS efficiently and securely within an AWS environment.
Most Important Ideas/Facts
1. Purpose and Scope of CIS Onboarding
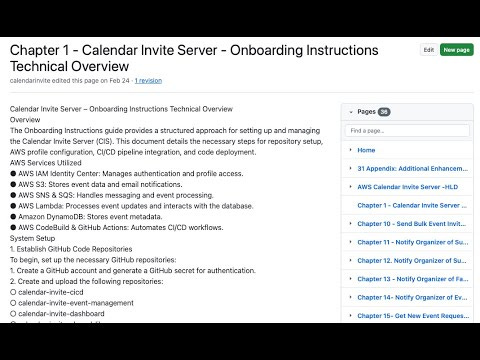
The "Onboarding Instructions guide provides a structured approach for setting up and managing the Calendar Invite Server (CIS)." Its primary goal is to detail "the necessary steps for repository setup, AWS profile configuration, CI/CD pipeline integration, and code deployment." This indicates a comprehensive guide designed for new team members or those responsible for deploying and maintaining the system.
2. Core AWS Services Utilized
The CIS leverages a suite of AWS services to ensure scalability, reliability, and automation. Key services include:
AWS IAM Identity Center: "Manages authentication and profile access." This is crucial for secure access control.
AWS S3: "Stores event data and email notifications." S3 provides highly durable and scalable object storage.
AWS SNS & SQS: "Handles messaging and event processing." These services enable asynchronous communication and a decoupled architecture.
AWS Lambda: "Processes event updates and interacts with the database." Lambda is used for serverless compute, executing code in response to events.
Amazon DynamoDB: "Stores event metadata." DynamoDB is a fast, flexible NoSQL database service for all applications that need consistent, single-digit millisecond latency at any scale.
AWS CodeBuild & GitHub Actions: "Automates CI/CD workflows." These are central to the automated build, test, and deployment process.
3. System Setup Requirements
A clear initial setup is required, involving both GitHub and AWS configurations:
GitHub Code Repositories: The process begins with establishing several GitHub repositories:
calendar-invite-cicd (Core infrastructure and deployment)
calendar-invite-event-management (Event processing and calendar logic)
calendar-invite-dashboard (Dashboard UI and supporting services)
calendar-invite-shared-library (Common shared functions and utilities) A GitHub account and a "GitHub secret for authentication" are prerequisites.
AWS Profile Configuration for Sceptre: This involves logging into AWS IAM Identity Center and configuring the AWS CLI for SSO, specifying us-west-2 as the region, and selecting appropriate accounts (dev or prod) with "AdministratorAccess" IAM roles. Profile names must be updated to "calendar-invite-dev" and "calendar-invite-prod" in infra/config.yaml and prod/config.yaml respectively.
4. CI/CD Pipeline Integration
The CI/CD pipeline is a critical component for automated deployments:
GitHub Actions and AWS CodeBuild: These are integrated, requiring updates to "sceptre-launch.yaml to reference correct GitHub accounts and repositories and modification of .gitmodules and .github/workflows/main.yaml.
Sceptre Deployments: Infrastructure components are launched using the command sceptre launch infra -y.
5. Code Management and Deployment Workflow
A structured approach to code changes and releases is enforced:
Version Control & Branching Strategy: "Use short-lived feature branches for development." All changes must go through "Pull Requests (PRs)," which "trigger GitHub Actions for linting and testing."
Deployment Workflow: New application versions are deployed by creating a Git tag: git tag -am “Release vX.x.x” X.x.x followed by git push origin X.x.x. This action "triggers AWS CodeBuild, updating the AWS Serverless Application Repository."
6. Repository Structure
The document clearly defines the purpose of each primary repository:
.aws/ and .github/: CI/CD configuration files.
calendar-invite-cicd/: Core infrastructure and deployment configurations.
Calendar-invite-dashboard/: Dashboard UI and supporting services.
Calendar-invite-event-management/: Event processing and calendar logic.
Calendar-invite-shared-library/: Common shared functions and utilities.
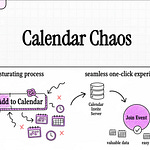
7. Event Processing Flow
The end-to-end event processing within CIS is detailed:
Email Handling: "SES receives an email and stores it in S3."
Event Notification: "SNS triggers a SQS queue, passing event data."
Lambda Processing: "Lambda retrieves SQS messages and updates DynamoDB," and subsequently "Triggers notifications via SES."
8. Security Considerations
Security is built into the architecture:
IAM Role Restrictions: "Access is limited to authorized roles."
Data Encryption: "Ensures secure data transmission and storage."
Access Control: "Tenant-based filtering enforces data isolation."
Conclusion
The "Calendar Invite Server – Onboarding Instructions Technical Overview" provides a comprehensive guide for deploying and managing the CIS. It highlights a serverless, event-driven architecture heavily reliant on AWS services, with a strong emphasis on automated CI/CD and robust security practices. The detailed steps for repository setup, AWS configuration, and deployment workflow ensure an "efficient and scalable method" for managing the Calendar Invite Server.
https://github.com/calendarinvite/calendarinviteserver/wiki/Chapter-1-%E2%80%90-Calendar-Invite-Server-%E2%80%90-Onboarding-Instructions-Technical-Overview
Calendar Invite Server (CIS) Onboarding Study Guide
Overview
This study guide is designed to help you understand the core components, setup procedures, and operational workflows of the Calendar Invite Server (CIS) as detailed in its Onboarding Instructions Technical Overview. The CIS is a system built on AWS services to manage and process calendar event invitations.
Study Guide
I. Introduction to Calendar Invite Server (CIS)
Purpose: Understand the primary goal of the CIS, which is to provide a structured approach for setting up and managing calendar invite processes.
Key Functionalities: Identify the main areas covered by the onboarding guide: repository setup, AWS profile configuration, CI/CD pipeline integration, and code deployment.
II. AWS Services Utilized
Authentication & Access:AWS IAM Identity Center: How is it used for managing authentication and profile access?
Data Storage: AWS S3: What type of data does S3 store within the CIS architecture?
Amazon DynamoDB: What is DynamoDB's role in storing event metadata?
Messaging & Event Processing: AWS SNS (Simple Notification Service): How does SNS contribute to event processing?
AWS SQS (Simple Queue Service): How does SQS integrate with SNS and Lambda for message handling?
AWS Lambda: What is the primary function of Lambda in the event processing flow?
CI/CD & Automation:AWS CodeBuild: How does CodeBuild automate CI/CD workflows?
GitHub Actions: How does GitHub Actions complement CodeBuild in CI/CD?
III. System Setup Procedures
GitHub Code Repositories: Prerequisites - What is required to set up GitHub repositories?
Repository List: Be able to list the four essential GitHub repositories for the CIS program.
AWS Profile Configuration for Sceptre: Tool Used: What tool is mentioned explicitly for AWS profile configuration?
SSO Configuration: Understand the steps for configuring AWS CLI SSO, including URL, region, authentication, and IAM roles.
Profile Naming Convention: How are profile names updated to distinguish between development and production environments?
IV. CI/CD Pipeline Integration
GitHub Actions and AWS CodeBuild Setup: Configuration Updates: What specific files/configurations need to be modified to link GitHub references?
Running Sceptre Deployments:Command: Know the Sceptre command used to launch infrastructure components.
V. Code Management and Deployment
Version Control & Branching Strategy: Branching Model: Describe the recommended branching strategy.
Commit Workflow: How are changes committed, and what triggers occur through this process?
Deployment Workflow:Command: What Git command is used to deploy a new application version?
Deployment Trigger: What AWS service is triggered by this deployment command?
VI. Repository Structure
Key Repositories and their Functions: Understand the purpose of each of the five listed repository types (.aws/ and .github/, calendar-invite-cicd/, calendar-invite-dashboard/, calendar-invite-event-management/, calendar-invite-shared-library/).
VII. Event Processing Flow
Email Handling: Initial Step - Where Do Incoming Emails First Go?
Event Notification: Messaging Sequence: Describe the flow from email receipt to message queue.
Lambda Processing: Processing Steps: What does Lambda do with SQS messages, and what follow-up action does it take?
VIII. Security Considerations
Core Security Principles: Identify and explain the three primary security considerations mentioned: IAM Role Restrictions, Data Encryption, and Access Control.
IX. Summary
Key Benefits: Recap the main advantages of the CIS onboarding process, such as efficiency, scalability, seamless AWS integration, robust event processing, and automated CI/CD.
Quiz: Calendar Invite Server Onboarding
Answer the following questions in 2-3 sentences each.
What is the primary purpose of the Calendar Invite Server (CIS) Onboarding Instructions guide?
Which two AWS services are primarily responsible for handling messaging and event processing within the CIS architecture?
List two of the four essential GitHub repositories that need to be created for the CIS system.
Describe the process of configuring AWS CLI SSO for Sceptre, explicitly mentioning the authentication step.
What is the recommended branching strategy for development in the CIS, and what triggers are associated with Pull Requests (PRs)?
How does an application version deployment get triggered in the CIS workflow?
What is the primary function of the calendar-invite-event-management/ repository?
Briefly explain the initial two steps of the event processing flow, from email receipt to notification.
Name and describe one of the security considerations implemented in the CIS system.
What role do AWS CodeBuild and GitHub Actions play in the CIS's CI/CD pipeline together?
Answer Key
The primary purpose of the Calendar Invite Server (CIS) Onboarding Instructions guide is to provide a structured approach for setting up and managing the Calendar Invite Server. It outlines the necessary steps for setting up a repository, configuring an AWS profile, integrating a CI/CD pipeline, and deploying code.
AWS SNS (Simple Notification Service) and AWS SQS (Simple Queue Service) are primarily responsible for handling messaging and event processing within the CIS architecture. SNS triggers an SQS queue, passing event data for subsequent processing.
Two of the four essential GitHub repositories are calendar-invite-cicd and calendar-invite-event-management. The other two are calendar-invite-dashboard and calendar-invite-shared-library.
To configure AWS CLI SSO for Sceptre, one first runs aws configure sso, provides the AWS IAM Identity Center start URL, and sets the region. Authentication is then performed via a browser, where the appropriate account (dev or prod) is selected, and IAM roles are ensured to be properly assigned.
The recommended branching strategy for development in the CIS is to use short-lived feature branches. All changes must be committed through Pull Requests (PRs), which in turn trigger GitHub Actions for linting and testing.
An application version deployment in the CIS workflow is triggered by tagging the Git repository with a release version (e.g., git tag -am “Release vX.x.x” X.x.x) and then pushing that tag to the origin (git push origin X.x.x). This action subsequently triggers AWS CodeBuild.
The calendar-invite-event-management/ repository is responsible for housing the event processing and calendar logic. This includes the core functionalities related to managing and processing calendar events within the system.
In the event processing flow, the initial step involves SES (Simple Email Service) receiving an email, which it then stores in S3. Following this, SNS (Simple Notification Service) triggers an SQS (Simple Queue Service) queue, passing the relevant event data for further processing.
One security consideration is IAM Role Restrictions, which ensures that access to the CIS system is limited to authorized roles only. Another is Data Encryption, which guarantees secure transmission and storage of data. Access Control, enforcing tenant-based filtering for data isolation, is also a key consideration. (Any one of these is acceptable).
AWS CodeBuild and GitHub Actions together automate CI/CD workflows in the CIS. GitHub Actions are triggered by Pull Requests for linting and testing, while AWS CodeBuild is triggered by Git tags during deployment to update the AWS Serverless Application Repository.
Essay Format Questions
Discuss the critical role of CI/CD pipeline integration in the efficient and scalable management of the Calendar Invite Server. Elaborate on how GitHub Actions, AWS CodeBuild, and Sceptre collectively contribute to this automation.
Detail the end-to-end event processing flow within the CIS, starting from email handling to database updates and subsequent notifications. Explain how various AWS services interact to facilitate this process.
Analyze the security considerations outlined for the Calendar Invite Server. Explain how IAM Role Restrictions, Data Encryption, and Access Control work together to secure the system and its data.
Describe the system setup requirements for the Calendar Invite Server, focusing on both GitHub repository establishment and AWS profile configuration. Explain why each step is essential for successful onboarding.
Compare and contrast the functions of the four main GitHub repositories (calendar-invite-cicd, calendar-invite-event-management, calendar-invite-dashboard, calendar-invite-shared-library) in the Calendar Invite Server architecture. How do they collectively form a cohesive system?
Glossary of Key Terms
AWS (Amazon Web Services): A comprehensive, broadly adopted, and widely used cloud platform, offering over 200 fully featured services from data centers globally. The CIS is built on various AWS services.
AWS IAM Identity Center: An AWS service that centralizes the management of SSO (Single Sign-On) access to multiple AWS accounts and cloud applications. Used for authentication and profile access in CIS.
AWS S3 (Simple Storage Service): An object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. Used by CIS to store event data and email notifications.
AWS SNS (Simple Notification Service): A highly available, durable, secure, fully managed pub/sub messaging service that enables you to decouple microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications. Used for event notifications in CIS.
AWS SQS (Simple Queue Service): A fully managed message queuing service that enables you to decouple and scale microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications. Handles messaging and event processing in CIS.
AWS Lambda: A serverless, event-driven compute service that lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers. Processes event updates and interacts with the database in CIS.
Amazon DynamoDB: A fully managed, serverless, key-value NoSQL database designed to run high-performance applications at any scale. Stores event metadata in CIS.
AWS CodeBuild: A fully managed continuous integration service that compiles source code, runs tests, and produces software packages that are ready to deploy. Automates CI/CD workflows in CIS.
GitHub Actions: A platform that allows you to automate tasks within your software development life cycle. Used with AWS CodeBuild for CI/CD workflows in CIS, particularly for linting and testing via Pull Requests.
CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment): A method to deliver apps to customers by introducing automation into the stages of app development.
Sceptre: A tool for managing multiple AWS CloudFormation stacks. Used in CIS for AWS profile configuration and launching infrastructure components.
GitHub Secret: An encrypted environment variable that you create in a repository or organization, used to store sensitive information like authentication tokens.
Pull Request (PR): A method for submitting changes to a project and requesting that they be reviewed and merged into the main codebase. In CIS, PRs trigger GitHub Actions for linting and testing.
Feature Branch: A short-lived branch in a version control system used for developing a specific new feature or improvement without affecting the main codebase until it's ready.
Git Tag: A marker that assigns a human-readable name to a specific commit in Git, often used to mark release points (e.g., v1.0.0) and used in CIS to trigger deployments.
AWS Serverless Application Repository: A collection of serverless applications that developers can deploy to their AWS accounts. AWS CodeBuild updates this repository as part of the CIS deployment workflow.
AWS SES (Simple Email Service): A cloud-based email sending service designed for digital marketers and application developers to send marketing, notification, and transactional emails. Receives and sends emails in CIS.